early childhood cluster

Assessment Workbook 1
CHC30113 Certificate III in Early Childhood Education and Care

Children’s Health and Safety
V3.1 Produced 8 August 2017
Copyright © 2016 Compliant Learning Resources. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system other than pursuant to the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 (Commonwealth), without the prior written permission of
Compliant Learning Resources
Version control & document history
| Date | Summary of modifications made | Version |
| 14 August 2019 | Version 1 final produced following assessment validation. | v1.0 |
| 16 April 2014 | Changes to wording and clarification of benchmarks in questions. A1,A3a,b,A14,A25,B10,C10 | v1.1 |
| 24 October 2014 | Minor clarifications in questions A14; removed B8(a) question similar with B7(d) | v1.2 |
| 18 November 2014 | Changes made throughout document | V1.3 |
| 3 December 2014 | Significant changes made to document following validation | V2.0 |
| 17 April 2015 | Minor revisions on Questions B1 and B16 | V2.1 |
| 18 July 2016 | Updates made throughout document | V2.2 |
| 9 August 2016 | Included CHCECE016 in the units of competency of this workbook. Added assessment items in the Project. | V3.0 |
| 8 August 2017 | Updated Intranet links | V3.1 |
This is an interactive table of contents. If you are viewing this document in Acrobat, clicking on a heading will transfer you to that page. If you have this document open in Word, you will need to hold down the Control key while clicking for this to work.
Table of Contents 3
Instructions 4
What is competency based assessment 5
The basic principles of assessing nationally recognised training 6
The principles of assessment 6
The dimensions of competency 7
Reasonable Adjustment 8
Cheating and Plagiarism 10
What is Cheating? 10
What is Plagiarism? 10
How do I avoid Plagiarism or Cheating? 10
The Units of Competency 11
HLTWHS001 - Participate in workplace health and safety 11
CHCECE016 Establish and maintain a safe and healthy environment for children 12
CHCECE002 - Ensure the health and safety of children 13
CHCECE004 - Promote and provide healthy food and drinks 15
Context for Assessment 16
Assessment Methods 17
Resources required for assessment 17
Presentation 18
Things to Consider: 18
If submitting your assessments please ensure that 18
Answering the Questions: 18
Assessment Workbook Coversheet 19
Knowledge Assessment 20
Part A 20
Part B 56
Part C 79
Case Studies – Part A 97
Case Study One 97
Case Study Two 98
Case Study Three 100
Case Studies – Part B 103
Project: Establish and Maintain A safe and healthy Environment for Children 125
Workbook Checklist 136
Required documents 137
Feedback 139
Instructions 4
What is competency based assessment 5
The basic principles of assessing nationally recognised training 6
The dimensions of competency 7
Reasonable Adjustment 8
Cheating and Plagiarism 10
The Units of Competency 11
Context for Assessment 16
Assessment Methods 17
Resources required for assessment 17
Presentation 18
Assessment Workbook Coversheet 19
Knowledge Assessment 20
Case Studies – Part A 94
Case Studies – Part B 100
Project: Establish and Maintain A safe and healthy Environment for Children 118
Workbook Checklist 129
Required documents 130
Feedback 132
InstructionsThe questions in the Knowledge Assessment are all in a short answer format. They address the underpinning knowledge and concepts relevant to the units of competency in this subject.
Case Studies are longer questions requiring creative thought processes and application of concepts to theoretical situations, while the Project sets out tasks to be delivered in an actual workplace setting.
Where applicable, you must answer all questions using your own words. However you may reference your learner guide, and other online or hard copy resources to complete this assessment.
You must attempt all assessments satisfactorily to achieve an overall award of competent.
Re-read the section on Plagiarism and Copying in your Welcome pack.
If you are currently working as part of an Early Childhood Education/Child Care team, you may answer these questions based on your own workplace. Otherwise consider what you should do if you were working as part of an Early Childhood Education/Child Care team you may refer to Sparkling Stars as an example.
The features of a competency based assessment system are:
It is focused on what learners can do and whether it meets the criteria specified by industry as competency standards.
Assessment should mirror the environment the learner will encounter in the workplace.
Assessment criteria should be clearly stated to the learner at the beginning of the learning process.
Assessment should be holistic. That is it aims to assess as many elements and/or units of competency as is feasible at one time.
In competency assessment a learner receives one of only two outcomes – competent or not yet competent.
The basis of assessment is in applying knowledge for some purpose. In a competency system, knowledge for the sake of knowledge is seen to be ineffectual unless it assists a person to perform a task to the level required in the workplace.
The emphasis in assessment is on assessable outcomes that are clearly stated for the trainer and learner. Assessable outcomes are tied to the relevant industry competency standards where these exist. Where such competencies do not exist, the outcomes are based upon those identified in a training needs analysis.
Definition of competency
Assessment in this context can be defined as:
The fair, valid, reliable and flexible gathering and recording of evidence to support judgement on whether competence has been achieved. Skills and knowledge (developed either in a structured learning situation, at work, or in some other context) are assessed against national standards of competence required by industry, rather than compared with the skills and knowledge of other learners.
Developing and conducing assessment, in an Australian vocational education and training context, is founded on a number of basic conventions:
The principles of assessment
Assessment must be valid
Assessment must include the full range of skills and knowledge needed to demonstrate competency.
Assessment must include the combination of knowledge and skills with their practical application.
Assessment, where possible, must include judgements based on evidence drawn from a number of occasions and across a number of contexts.
Assessment must be reliable
Assessment must be reliable and must be regularly reviewed to ensure that assessors are making decisions in a consistent manner.
Assessors must be trained in national competency standards for assessors to ensure reliability.
Assessment must be flexible
Assessment, where possible, must cover both the on and off-the-job components of training within a course.
Assessment must provide for the recognition of knowledge, skills and attitudes regardless of how they have been acquired.
Assessment must be made accessible to learners though a variety of delivery modes, so they can proceed through modularised training packages to gain competencies.
Assessment must be fair and equitable
Assessment must be equitable to all groups of learners.
Assessment procedures and criteria must be made clear to all learners before assessment.
Assessment must be mutually developed and agreed upon between assessor and the assessed.
Assessment must be able to be challenged. Appropriate mechanisms must be made for reassessment as a result of challenge.
The rules of evidence (from Training in Australia by M Tovey, D Lawlor)
When collecting evidence there are certain rules that apply to that evidence. All evidence must be valid, sufficient, authentic and current;
Valid
Evidence gathered should meet the requirements of the unit of competency. This evidence should match or at least reflect the type of performance that is to be assessed, whether it covers knowledge, skills or attitudes.
Sufficient
This rule relates to the amount of evidence gathered It is imperative that enough evidence is gathered to satisfy the requirements that the learner is competent across all aspects of the unit of competency.
Authentic
When evidence is gathered the assessor must be satisfied that evidence is the learner’s own work.
Current
This relates to the recency of the evidence and whether the evidence relates to current abilities.
The national concept of competency includes all aspects of work performance, and not only narrow task skills. The four dimensions of competency are:
Task skills
Task management skills
Contingency management skills
Job role and environment skills
Adapted Reasonable Adjustment in teaching, learning and assessment for learners with a disability - November 2010 - Prepared by - Queensland VET Development Centre
Reasonable adjustment in VET is the term applied to modifying the learning environment or making changes to the training delivered to assist a learner with a disability. A reasonable adjustment can be as simple as changing classrooms to be closer to amenities, or installing a particular type of software on a computer for a person with vision impairment.
Why make a reasonable adjustment?
We make reasonable adjustments in VET to make sure that learners with a disability have:
the same learning opportunities as learners without a disability
the same opportunity to perform and complete assessments as those without a disability.
Reasonable adjustment applied to participation in teaching, learning and assessment activities can include:
customising resources and assessment activities within the training package or accredited course
modifying the presentation medium learner support
use of assistive / adaptive technologies
making information accessible both prior to enrolment and during the course
monitoring the adjustments to ensure learner needs continue to be met.
Assistive / Adaptive Technologies
Assistive/adaptive technology means ‘software or hardware that has been specifically designed to assist people with disabilities in carrying out daily activities’ (World Wide Web Consortium - W3C). It includes screen readers, magnifiers, voice recognition software, alternative keyboards, devices for grasping, visual alert systems, digital note takers.
IMPORTANT NOTE
Reasonable adjustment made for collecting candidate assessment evidence must not impact on the standard expected by the workplace, as expressed by the relevant Unit(s) of Competency. E.g. If the assessment was gathering evidence of the candidates competency in writing, allowing the candidate to complete the assessment verbally would not be a valid assessment method. The method of assessment used by any reasonable adjustment must still meet the competency requirements.
What is Cheating?
Cheating within the context of the study environment means to dishonestly present an assessment task or assessment activity as genuinely representing your own understanding of and/or ability in the subject concerned.
Some examples of cheating are:
Submitting someone else’s work as your own. Whether you have that persons consent or not.
Submitting another author’s work as your own, without proper acknowledgement of the author.
To allow someone else to submit your own work as theirs.
To use any part of someone else’s work without the proper acknowledgement
There are other forms of cheating not contained in this list. These are merely given as some examples. If you are unsure about whether any particular behaviour would constitute plagiarism or cheating, check with your trainer prior to submitting your assessment work.
What is Plagiarism?
Plagiarism is a form of cheating and includes presenting another person or organisation’s ideas or expressions as your own. This includes, however is not limited to: copying written works such as books or journals, data or images, tables, diagrams, designs, plans, photographs, film, music, formulae, web sites, and computer programs.
How do I avoid Plagiarism or Cheating?
Students are advised to note the following advice to avoid claims of plagiarism or cheating:
Always reference other people’s work. You may quote from someone else's work (for example from websites, textbooks, journals or other published materials) but you must always indicate the author and source of the material.
Always reference your sources. You should name sources for any graphs, tables or specific data, which you include in your assignment.
You must not copy someone else's work and present it as your own.
You must not falsify assessment evidence.
Each unit of competency can be unbundled to reveal two key assessment components:
the performance criteria
specifying the required level of performance
the evidence guide
Describing the underpinning knowledge and skills that must be demonstrated to determine competence. It provides essential advice for assessment of the unit of competency in the form of:
critical aspects of evidence
the essential skills
the essential knowledge
An outline of the units of competency is included below. Note that some skills that are not able to be observed in the workplace during your Vocational Placement will be assessed utilising Case Studies and/or projects.
HLTWHS001 - Participate in workplace health and safety
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required for workers to participate in safe work practices to ensure their own health and safety, and that of others.
Follow safe work practices
Implement safe work practices
Contribute to safe work practices in the workplace
Reflect on own safe work practices
Foundation Skills
Reading – in order to accurately read and interpret workplace safety policies and procedures including safety signs, dangerous goods classifications and safety instructions
The remaining foundation skills essential to performance are explicit in the performance criteria of this unit
Performance Evidence
The candidate must show evidence of the ability to complete tasks outlined in elements and performance criteria of this unit, manage tasks and manage contingencies in the context of the job role.
There must be demonstrated evidence that the candidate has completed the following tasks at least once in line with state/territory WHS regulations, relevant codes of practice and workplace procedures:
contributed to a WHS meeting or inspection in workplace
conducted a workplace risk assessment and recorded the results
consistently applied workplace safety procedures in the day-to-day work activities required by the job role
followed workplace procedures for reporting hazards
followed workplace procedures for a simulated emergency situation.
Knowledge Evidence
The candidate must be able to demonstrate essential knowledge required to effectively complete tasks outlined in elements and performance criteria of this unit, manage tasks and manage contingencies in the context of the work role. This includes knowledge of:
state/territory legislation and how it impacts on workplace regulations, codes of practice and industry standards, including:
state/territory WHS authorities
rights and responsibilities of employers and workers, including duty of care
hazardous manual tasks
infection control
safety signs and their meanings, including signs for:
dangerous goods classifications
emergency equipment
personal protective equipment (PPE)
specific hazards such as sharps, radiation
hazard identification, including:
definition of a hazard
common workplace hazards relevant to the industry setting
workplace procedures for hazard identification
workplace emergency procedures
workplace policies and procedures for WHS
CHCECE016 Establish and maintain a safe and healthy environment for children
The unit describes the skills and knowledge to establish and maintain a safe and healthy environment for children.
This unit applies to educators working in a range of education and care services.
Support each child’s health needs
Provide for each child’s comfort
Promote and implement effective hygiene practices
Take steps to control the spread of infectious diseases
Ensure adequate supervision of children
Take precaution to protect children from harm
Develop plans to effectively manage incidents and emergencies
Performance Evidence
The candidate must show evidence of the ability to complete tasks outlined in elements and performance criteria of this unit, manage tasks and manage contingencies in the context of the job role. There must be demonstrated evidence that the candidate has completed the following tasks:
established and maintained an environment that is safe and healthy for children in at least once service, including:
communicating hazards and safety issues to appropriate persons within the service
coordinating emergency responses including evacuation plans
planning and coordinating supervision of children
promoting and monitoring safety practices, including administration of medicines and safe handling of food
coordinating appropriate procedures for handling infections and illnesses, including communicating with families
enacting strategies to support children to take increasing responsibility for their own health and physical wellbeing.
Knowledge Evidence
The candidate must be able to demonstrate essential knowledge required to effectively do the task outlined in elements and performance criteria of this unit, manage the task and manage contingencies in the context of the work role. These include knowledge of:
how to access:
the National Quality Framework
the National Quality Standards
the relevant approved learning framework
how to navigate through framework and standards documents to find areas relevant to this unit of competency
common childhood illnesses and appropriate responses
strategies for minimising risk
notifiable diseases
organisational standards, policies and procedures.
CHCECE002 - Ensure the health and safety of children
This unit describes the skills and knowledge to ensure the health and safety of children.
Support each child’s health needs
Provide opportunities to meet each child’s need for sleep, rest and relaxation
Implement effective hygiene and health practices
Supervise children to ensure safety
Minimise risks
Contribute to the ongoing management of allergies
Contribute to the ongoing management of asthma
Foundation Skills
Reading – in order to accurately read and interpret medication packaging and dosage instructions
Numeracy – in order to correctly calculate medication dosages for common measurements including milligrams (mg) and millilitres (ml)
The remaining foundation skills essential to performance are explicit in the performance criteria of this unit.
Performance Evidence
The candidate must show evidence of the ability to complete tasks outlined in elements and performance criteria of this unit, manage tasks and manage contingencies in the context of the job role. There must be demonstrated evidence that the candidate has completed the following tasks at least once:
consistently supported the health needs of the children in the service, including the following activities:
contributing to the provision of a clean and safe environment
recognising and responding to signs of illness of children, including signs and symptoms of asthma and anaphylaxis
reading and interpreting authorisation forms, medication labels, medical management plans and other relevant medical information
developing children’s awareness of safety
Knowledge Evidence
The candidate must be able to demonstrate essential knowledge required to effectively do the task outlined in elements and performance criteria of this unit, manage the task and manage contingencies in the context of the work role.
These include knowledge of:
how to access:
the National Quality Framework
the National Quality Standards
the relevant approved learning framework
how to navigate through framework and standards documents to find areas relevant to this unit of competency
how to undertake a risk analysis of toys and equipment
potential hazards to children, including medical conditions
children’s requirements for sleep and rest
environments that promote rest and sleep including light, noise, temperature and ventilation requirements
signs, symptoms and key characteristics of allergy/anaphylaxis
signs, symptoms and key characteristics of asthma
how to use an adrenalin auto injector for anaphylaxis
how children’s oral health impacts on their general health and well-being, including signs of tooth decay
safety issues and risk management strategies for children’s health and safety in a variety of contexts
basic home fire safety including high-risk groups, behaviour that contributes to fire injury and fatalities, and smoke alarm placement, installation and maintenance
organisational standards, policies and procedures.
CHCECE004 - Promote and provide healthy food and drinks
This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to promote healthy eating and ensure that food and drinks provided are nutritious, appropriate for each child and prepared in a safe and hygienic manner.
Promote healthy eating
Plan food and drinks that are nutritious and appropriate for each child
Maintain food safety while carrying out food-handling activities
Foundation Skills
Reading – in order to accurately read and interpret food labels and dietary requirements.
The remaining foundation skills essential to performance are explicit in the performance criteria of this unit.
Performance Evidence
The candidate must show evidence of the ability to complete tasks outlined in elements and performance criteria of this unit, manage tasks and manage contingencies in the context of the job role. There must be demonstrated evidence that the candidate has completed the following tasks:
planned and provided food and drink for children on at least three occasions, including:
identifying and responding to requirements related to food allergies, medical conditions and cultural and religious requirements
role-modelling healthy eating habits for children
ensuring safe handling, preparation and storage of food and drinks
creating a positive, relaxed environment during mealtimes
engaged children by involving them in menu planning and assisting in meal preparation
read and interpreted food labels to identify ingredients of concern and nutrition content.
Knowledge Evidence
The candidate must be able to demonstrate essential knowledge required to effectively do the task outlined in elements and performance criteria of this unit, manage the task and manage contingencies in the context of the work role. These include knowledge of:
how to access:
the National Quality Framework
the National Quality Standards
the relevant approved learning framework
how to navigate through framework and standards documents to find areas relevant to this unit of competency
United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child
code of ethics
food allergies, food intolerances, contamination and/or allergic reactions in meal preparation and possible reactions, including anaphylaxis
infant feeding requirements and guidelines
recommendations for healthy eating – Dietary Guidelines for Children and Adolescents in Australia and the Australian Guide to Healthy Eating, including Get Up and Grow: Healthy Eating and Physical Activity for Early Childhood resources
implications of poor diet including tooth decay, deficiencies, poor concentration, out of character behaviour
food-handling requirements, preventing microorganism contamination and/or allergic reactions
importance of addressing individual dietary needs and preferences with particular reference to specific cultural, religious or health requirements
organisational standards, policies and procedures.
Assessment for these units will be assessed through completion of Workbook One (1) and Workbook Seven (7).
Context for AssessmentTo complete the assessment in this workbook, students need to have access to their learning materials and the internet. The written questions and case studies may be completed wholly at the student’s home, or chosen place of study.
The project may be completed in the student’s vocational work placement.
Assessment for this unit will be assessed through completion of Assessment Workbook One (1) and the relevant section of Workbook Seven (7) Skills Journal.
Workbook One (1) will focus on three assessment methods:
Written Questions – based on the required knowledge component as described in the Instructions for Assessment
Case Studies – utilising the Sparkling Stars virtual Education and Care Service and activities set out in this workbook, provides detailed scenarios designed to assist completion of relevant tasks addressing underpinning skills and/or knowledge requirements
Project – A set of tasks designed to address underpinning skills and/or knowledge requirements
Further Assessments:
Workbook Seven (7) Skills Journal
Participant must attend Vocational Placement and maintain a log of tasks completed and signed off by supervisor in the workplace.
Resources required for assessmentTo complete the assessments in this workbook, the candidates will need access to:
Computer with internet access, internet browser, MS Word, and Adobe Acrobat Reader
One (1) piece of multimedia recording equipment such as:
Camcorder or camera
Voice recorder
Mobile phone or tablet
One (1) volunteer to assist in minor role-play
Things to Consider:
Only submit your workbook once all activities inside are complete. Should you have any questions regarding your assessments, or not understand what is required for you to complete your assessment, please feel free to ask your trainer.
Keep your answers succinct and make sure you are answering the question. Re-read the question after you have drafted up your response just to be sure you have covered all that is needed.
Your final assessment result will either be competent or not yet competent.
If submitting your assessments please ensure that
All assessment tasks within the workbook have been completed
You have proof read your assessment
| Answering the Questions: | |
| |
| |
| Assessments may not be processed if the above guidelines are not adhered to. To ensure your assessment is processed as quickly as possible, please follow these instructions. |
| WORKBOOK: | WORKBOOK 1 | ||
| TITLE: | Children’s Health and Safety | ||
| FIRST AND SURNAME: | Bikramjit Singh | ||
| PHONE: | 0420465840 | ||
| EMAIL: | |||
| Please read the Candidate Declaration below and if you agree to the terms of the declaration sign and date in the space provided. | |||
| By submitting this work, I declare that:
| |||
| Name :bikramjit singh | Signature: bikramjit singh | Date: | |
Part A
| 1. You are required to demonstrate how to access the following in relevance to ensuring the health and safety of children in the workplace:
Guidance: Fill out each section in the table below using relevant information from the National Quality Framework, The National Quality Standards, and the relevant approved learning framework. | |
| a. Under the NQS there are a number of standards that are relevant to the safety of children in an Early Childhood Education and Care service. What are the 3 main Standards that support this? | i. Standard 2.1 Each child help is promoted. ii. Standard 2.2 Health eating and physical activity are embedded in the program for children. iii. Standard 2.3 Each child is protected. |
| b. How is the health and safety of children related to the EYLF? Guidance: Outline which of the five Outcomes addressed in the EYLF most relates to the health and safety of children and explain why. | Outcome 3: Children have a strong sense of wellbeing. Physical wellbeing contributes to children`s to concentrate, cooperate and learn. A strong sense of health and wellbeing supported by good nutrition and an active lifestyle provides children with confidence; energy and optimism that contribute their ability to concentrate cooperate and learn. Through a widening network of secure relationships, children develop confidence and feel respected and valued. |
| c. What practice does the Guide to the EYLF recommend that educators use to raise and debate issues relating to curriculum quality, equity and children’s wellbeing? | The EYLF is the Victorian state framework which is affiliated with the national quality framework (NQF). EYLF focuses on three integrated components: The early childhood setting Family and community and the child EYLF elements concentrate on belonging, being and becoming. |
| d. Review the practice section outlined in the Framework for School Age Care in Australia (FSAC). This section outlines that “nutrition and safety” are seen as important for educators to consider in relation to ___________. (fill in the gap) Which practice does this fall under? | Children`s health and safety |
| e. In the FSAC, it states that educators can facilitate “Children take increasing responsibility for their own health and physical wellbeing” by engaging children in what activities that relate to safety? | Children should wash their hands (health and safety) After going to toilet. Blowing our nose. After playing outside. Before we eat. |
| f. Which two National Regulations does the following statement relate to? “minimise risks to children, an education and care service or a family day care educator must implement: • adequate health and hygiene practices • safe practices for handling, preparing and storing food.” Guidance: Refer to the National Quality Framework website. | Children`s health and safety. Physical environment. 2.1..3 Effective hygiene practices are promoted and implemented. |
| g. Which National Regulation does the below statement relate to? “While attending an approved service, children must have access to safe drinking water at all times, and have food and drinks available throughout the day” Guidance: Refer to the National quality framework website. | Children`s health and safety. |
| 2. In your role as an Early Childhood Education and Care worker, you will need to check toys and equipment for potential risk and hazards that may cause harm to children.
Guidance: Include reporting procedures and the designated person that you would report to according to organizational procedures. Refer to the Hierarchy of Control. |
| a. Steps involved in conducting a risk analysis on toys 1. Identify the hazards. 2. Decide who could be harmed and in what way. 3. Establish Control Measures. 4. Record the findings of your assessment and inform those at risk of the controls. 5. Review the Risk Assessment on a regular basis. |
| b. Steps you would take if you identified a toy or piece of equipment that presented a WHS hazard with an extreme risk
|
| c. Policies and/or procedures to reference for WHS issues
|
| 3. In your role as an Early Childhood Education and Care worker, you will need to implement effective hygiene and health practices in many aspects of practice. |
i. The centre (overall) ii. Kitchen iii. Outdoor Environment iv. Indoor Environment v. Toilets Guidance: Make sure you discuss the risks associated with not maintaining these environments and associated risks. | ||
| Area | Importance of maintaining a clean and healthy environment | Associated Risk |
| i. The Centre (overall) |
|
|
| ii. Kitchen |
|
|
| iii. Outdoor Environment |
|
|
| iv. Indoor Environment |
|
|
| v. Toilets |
|
|
i. Education and Care Services National Regulations ii. National Quality Standards (NQS) iii. Early Years Learning Framework (EYLF) iv. Framework for School Aged Care in Australia (FSAC) Guidance: You need to review these frameworks and identify which section, standard or outcomes, address WHS requirements, policies and procedures. | |
| i. Education and Care Services National Regulations |
|
| ii. National Quality Standards (NQS) |
|
| iii. Early Years Learning Framework (EYLF) |
|
| iv. Framework for School Aged Care in Australia (FSAC) |
|
| 4. Complete the table below explaining the cleaning procedures for each, and provide one reason for the importance of the cleaning procedure. | ||||
| Items | Cleaning Procedure | Reason | Cleaning Product | Storage of Cleaning Product |
| Toys |
|
|
|
|
| Items | Cleaning Procedure | Reason | Cleaning Product | Storage of Cleaning Product |
| Floors |
|
|
|
|
| Items | Cleaning Procedure | Reason | Cleaning Product | Storage of Cleaning Product |
| Toilets, potties and bathroom area |
|
|
|
|
| 5. List two (2) personal hygiene policies or procedures that you must follow to limit cross-contamination when preparing food, and explain why they are important in relation to Work Health and Safety. | |
| Personal Hygiene Procedure | Explanation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6. As a child care worker, you will need to help provide suitable rest and sleep environments for children. For each of the following points, describe why these are important and what you would check to ensure the rest environment is set up appropriately: i. Ventilation ii. Lighting iii. Heating/cooling iv. Hygiene v. Safety | ||
| Importance | Checks that need to be done | |
| i. Ventilation |
|
|
| ii. Lighting |
|
|
| iii. Heating / cooling |
|
|
| iv. Hygiene |
|
|
| v. Safety |
|
|
| 7. As an Early Childhood Education and Care worker, you are required to ensure that sleep and rest opportunities are provided for, and that there are appropriate opportunities to meet each child’s need for sleep, rest, and relaxation.
Guidance: Refer to the SIDS and Kids Website. |
| a) Which standards in the NQS relate to sleep and rest?
|
| b) What section of the National Regulation covers sleep and rest?
|
| c) Ways to promote safe sleep for babies and reduce the risk of sudden Death Syndrome (SIDS) i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. |
| 8. Suppose you are an assistant educator at Sparkling Stars Childcare Centre. Write a short email below, sharing information about a child’s rest and sleep. Address the email to Mrs. Anna Parkinson, the mother of George, a four-year-old student attending your class. George is a new student who has been attending the centre for two weeks. His mother would like a general update about your observations regarding her son’s daily routines, including sleep and rest. Guidance: You may write fictional but realistic information about George that is relevant to the report you will send to his mother and within the typical scope of an assistant educator, such as George’s behaviour (such as his difficulty or ease in sleeping, attitude towards staff and other children, etc.) You do not need to send an actual email to the address indicated below. | |
| To | Anna Parkinson <[email protected]> |
| From | Your name and email |
| Subject | Any appropriate subject |
| Message |
|
| 9. It is a requirement that centres must provide appropriate quiet play activities for children who do not want to sleep or rest. Describe five (5) alternative activities. |
| i. ii. iii. iv. v. |
| 10. In an Early Childhood Education and Care setting, you must respect children’s needs for privacy during any toileting and dressing and undressing times. Describe three (3) ways in which you would maintain this. |
| i. ii. iii. |
| 11. You are required to ensure children’s and families’ individual clothing needs and preferences are met, to promote children’s comfort, safety and protection within the scope of the service requirements for children’s health and safety. a) List three (3) examples of instances where you would inform parents of clothing that the centre considers to be inappropriate or unsuitable for children to wear while attending the centre? b) List two (2) examples of ways in which staff can ensure that children are dressed appropriately for Indoor/Outdoor Environmental conditions and temperatures. |
| a) Examples of instances where you would inform parents of clothing that the centre considers to be inappropriate or unsuitable for children to wear while attending the centre i. ii. iii. |
| b) Examples of ways in which staff can ensure that children are dressed appropriately for Indoor/Outdoor Environmental conditions and temperatures i. ii. |
| 12. When children are playing or travelling outdoors you must ensure they are safe at all times.
Guidance: If you have not been to a child care centre yet, examine the sun protection policy on the Sparkling Stars Childcare Centre intranet. Sparkling Stars Childcare Centre Sun Care Policy (Username: learner Password: studyhard)
Guidance: Refer to the Cancer Council Website. |
| a) Sun protection/ safety procedures
|
| b) How to explain sun safety to children
|
| 13. As a child care worker, you will be required to set up a variety of play environments for children. a) List five (5) checks you should perform when setting up a play environment. b) Describe the considerations when choosing equipment that is suitable for the age group of children you’re working with. |
| a) Checks to perform when setting up a play environment i. ii. iii. iv. v. |
| b) Considerations when choosing equipment
|
| 14. Children must be supervised by ensuring that they are in sight or hearing distance at all times.
Guidance: Describe how you would liaise with colleagues to ensure there was adequate supervision at all times. |
| a) Ratios for supervising children in an Early Education and Care setting
|
| b) Process you would follow if you found that you have children with additional needs in your care
|
| c) Ways that you can ensure there is adequate supervision at all times i. ii. iii. iv. |
| 15. Describe how you can explain hazards in the environment to children. Guidance: Include in your answer how awareness of these hazards is very important in relation to a child’s health and safety, hygiene, and general well- being. |
|
|
| 16. As a childcare worker, it is important to ensure that play environments are clean and safe for children.
Guidance: Include how you discuss health and hygiene issues in relation to safe play. |
| a) Strategies you can use to communicate the rules for safe play to the children in the group i. ii. |
| b) How you implement the rules for safe play
|
| 17. As a child care worker, you will sometimes have to deal with children who are unwell.
|
| a) |
| b) |
| c) |
| d) |
| 18. You are required to consistently implement the service policies for the exclusion of ill children.
|
| a) Infectious diseases that would cause the centre to exclude a child i. ii. iii. iv. v. |
| b)Precautions to take if a child is suspected to be infectious i. ii. iii. |
| 19. As a child care worker, you will often have to deal with children who have allergies/anaphylaxis or asthma. |
|
| a. |
|
| b. |
|
| c1. c2. c3. |
|
| d. |
|
| e1. e2. e3. e4. e5. |
|
| f. Adrenalin Auto Injector |
| How to give Anapen
|
| How to give EpiPen
|
|
| g1. g2. g3. |
| 20. As a child care worker, you will sometimes be required to assist in administering medication to children. |
|
| a1. a2. a3. a4. a5. a6. |
|
| b. |
|
| c. |
| 21. Fill out the table below and explain what action you would take to reduce the risk associated with each of the hazards listed in the table below. | |
| Hazard | Action to be taken |
| A parent has left a bottle of antibiotics on the teacher’s desk |
|
| The rubbish bin in a room is overflowing |
|
| A colleague is serving food to children with bare hands |
|
| A child is playing in the midday sun without a hat or sunscreen |
|
| You notice during one of the meal times that a child with a nut allergy has been given a muesli bar that may contain nuts. |
|
| You enter a room after lunch and find there is food on the floor |
|
| A cleaning product has been left on the shelf in the classroom |
|
| The collage trolley in a room is partially blocking a fire exit |
|
| During lunchtime, you notice that a child with coeliac disease has been given regular bread in their sandwich, instead of gluten free bread. |
|
| 22. The National Quality Standard (NQS) Quality Area 2.3 states that “each child is protected” and Element 2.3.1 states that “Children are adequately supervised at all times”. It is critical that staff ensure that all children are in sight or hearing distance at all times. Guidance: Refer to the National Quality Standard (National Law and National Regulations). |
| a) Explain how you would follow service procedures for the safe collection of each child, ensuring they are released to authorised people. |
| a. How you would follow service procedures for the safe collection of each child
|
| b) What must occur if a child is missing or cannot be accounted for? |
| b. If a child is missing or cannot be accounted for
|
| 23. List three (3) ways in which you can safely manage the use, storage and labelling of dangerous products. |
| i. ii. iii. |
| 24. Understanding your role in fire safety is an important factor in keeping children safe in Early Childhood Education and Care. Using the table below, explain in your own words the following aspects of basic home fire safety: | |
| Fire spread and speed |
|
| Heat transfer |
|
| Radiation |
|
| Convection |
|
| Conduction |
|
| Combustible fuels |
|
| Sources of heat |
|
| Open flames/sparks |
|
| Electrical equipment |
|
| Hot surfaces |
|
| Smoking materials |
|
| Role of fire services |
|
| Identify high-risk groups in basic home for safety |
|
| Identify behaviour that may contribute to fire injury and fatalities (List three per category.) | Older People
Children under 5 years of age
People who experience social and financial disadvantage
People who are afflicted by alcohol and other drugs
|
| Why smoke alarm is important |
|
| Smoke alarm placement |
|
| Installation |
|
| Maintenance |
|
Part B
| 1. Research and access the following legislation, in relevance to promoting and providing healthy food and drinks:
Guidance: Once you have done the appropriate research, fill out the table below in the spaces provided. | |
| a. Under the NQS there are a number of standards that are relevant to promoting and providing healthy food and drinks in an Early Childhood Education and Care service. What are the main Standards and regulations that support this? |
|
| b. Where can you access the “Get up and Grow” resources for promoting and providing healthy food and drinks |
|
| c. Where can you access the “Australian Dietary Guidelines” |
|
| 2. Describe two (2) different activities you can do with children to help them learn about healthy eating. |
| i. |
| ii. |
| 3. Describe how you can ensure children are provided with sufficient healthy food and water in the below situations:
Guidance: In your answers, discuss how you will ensure individual children’s dietary and calorie intake needs are met. |
| a) How you can ensure meals are provided for the children by the centre How will you ensure individual children’s dietary and calorie intake needs are met by these meals?
|
| a) How you can ensure families provide food for the children How will you ensure individual children’s dietary and calorie intake needs are met by the food provided by the family?
|
| 4. As a childcare worker, it is important to act as a role model in implementing healthy eating and nutrition practices during meal times.
|
| a) Why is it important to interact with children during meal times?
|
| b1) b2) b3) b4) |
| 5. List three (3) strategies you could use to help educate families about healthy eating. Guidance: Provide an example of one of the strategies you suggested. |
| Strategies for educating families about healthy eating i. ii. iii. |
| 6. In a child care service, you will need to cater for children’s individual dietary needs.
|
| a) |
| b) |
| c) |
| d) |
| 7. Describe how children’s oral health, including signs of tooth decay impacts on their general health and well-being. |
|
|
| 8. Answer the following questions:
|
| a) Recommended steps in preparing formula
|
| b) Standards of Infant formula’ in Australia
| ||||||||||
| c) What is the WHO code and how does it affect staff in an Early Childhood Education and Care service?
| ||||||||||
| d) Recommended sterilisation methods for preparing infant feeding equipment List the steps of the different methods.
| ||||||||||
| e)
| ||||||||||
| f) Types of formula available for treating or preventing allergic reactions Are they effective in treating allergic reactions?
|
| g) Recommendations for minimising the risk of allergy in infants with a family history of allergies
|
| 9. Consider a mother who wants to continue breastfeeding her baby whilst attending your child care service. |
|
| a1. a2. a3. |
|
| b. Benefits of breastfeeding
|
|
| c. Recommended steps for storing breast milk under the Infant Feeding Guidelines
|
| |||
| Breast milk status | Storage at room temperature (26°C or lower) | Storage in refrigerator (5°C or lower) | Storage in freezer |
| Freshly expressed into sterile container |
|
|
|
| Previously frozen (thawed) |
|
|
|
| Thawed outside refrigerator in warm water |
|
|
|
| Infant has begun feeding |
|
|
|
| 10. List the three (3) key points to consider when introducing solid foods to infants. |
| i. ii. iii. |
| 11. Describe two (2) ways you, as an assistant educator, can contribute to the healthy eating/nutrition policies and procedures at your child care service. |
| i. ii. |
| 12. Safe food handling is paramount in Early Childhood education and care services.
Guidance: At least two (2) must be provided.
|
| a) |
| b1) b2) b3) |
| c1) c2) c3) c4) c5) c6) c7) c8) |
| d) |
| 13. Below are dietary guides of two foods. Write a paragraph to explain which food is the healthier choice. Guidance: From the two options, pick the healthier choice in respect to: i. Saturated Fat Content ii. Salt Content iii. Sugar Content iv. Fibre Content | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14. List four (4) procedures that should be in place to protect children from exposure to food allergens. |
| i. ii. iii. iv. |
| 15. What are the ‘Five Guidelines’ from the Australian Dietary Guidelines. |
| 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
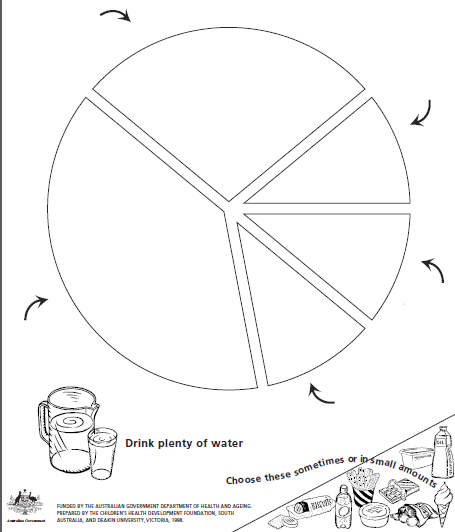
| 16. Label the different sections of the graph below indicating the recommended portions of food groups we should eat each day. Guidance: This graph was sourced from “The Australian Guide to Healthy Eating” | ||
| 1 |
|
|
| 2 |
| |
| 3 |
| |
| 4 |
| |
| 5 |
| |
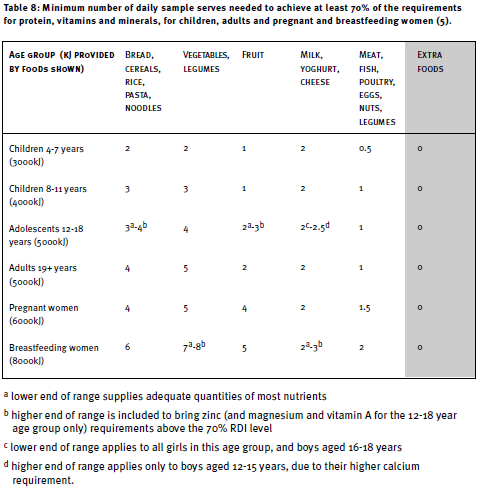
| 17. From the table below determine the minimum number of daily serves for each of the selected children.
|
| a) |
| b) |
| c) |
| 18. The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child and the ECA Code of Ethics relate to codes of practice that should be followed when working with children. a) Outline the section in the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child that refers to ensuring children’s health and safety, in relation to food and water. b) Outline the section in the ECA Code of Ethics that relates to creating safe and healthy environments for children. Guidance: Refer to the United Nations Rights of the Child website and the ECA Code of Ethics website. |
| a) United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child
|
| b) ECA Code of Ethics
|
| 19. Give an example of each of the points below and describe in your own words why it is important to address the individual dietary needs and preferences of children in respect to: a) specific cultural requirements b) religious requirements c) health requirements |
| a) |
| b) |
| c) |
Part C
| 1. In the following table, name the relevant legislations, regulations, codes and standards and how they impact on WHS/OHS in the workplace: a) The act b) workplace regulations, c) codes of practice d) industry standards e) State/territory WHS authorities f) Rights and responsibilities of employers and workers g) duty of care h) Hazardous manual tasks i) Infection control j) Policies and procedures in Early Childhood Education and Care | |
| Regulation, Law or Code | How it Impacts on WHS/OHS in the Workplace |
| a) The Act |
|
| b) Workplace regulations |
|
| c) Codes of practice |
|
| d) Industry standards Give 2 examples. | i. ii. |
| e) State/ territory WHS authorities |
|
| f) Rights and responsibilities of employers and workers Give 3 examples each. | Employers i. ii. iii. Workers i. ii. iii. |
| g) Duty of care Give 3 examples. | i. ii. iii. |
| h) Hazardous manual tasks Give 3 examples. | i. ii. iii. |
| i) Infection control |
|
| j) Policies/ Procedures Give 3 examples. | i. ii. iii. |
| 2. It is important that you can identify hazards in an Early Childhood Education and Care service.
|
| a) |
| b) |
| c1) c2) c3) c4) c5) |
| d1) d2) |
| e1) e2) |
| 3. Answer the following questions about risk. a) Provide the definition of a risk. b) Describe the risk involved with one of the hazard examples you provided in question 2c above and how you would manage that risk. |
| a) |
| b) |
| 4. It is every educator’s responsibility to help ensure the environment is safe for themselves, their colleagues and the children, and visitors attending the centre. Give three (3) examples of how you can fulfil this responsibility. |
| i. ii. iii. |
| 5. Identify two (2) ways you can stay up-to-date with Workplace Health and Safety information. |
| i. ii. |
| 6. Review the environment in this picture. Complete the following table to identify 3 of the hazards present in this indoor environment:
| |||
| Identified hazard | Associated risk | Severity of risk | Control and reporting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7. Complete the following table in relation to three (3) of the hazards present in the outdoor environment pictured:
|
| Identified hazard | Associated risk | Severity of risk | Control and reporting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 8. Complete the following table in relation to three (3) of the hazards present in the storage environment pictured:
|
| Identified hazard | Associated risk | Severity of risk | Control and reporting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 9. Identify the following safety signage and their meanings: a) Dangerous goods classifications. b) Common first aid and safety signage. | ||
| a) Dangerous goods classifications | ||
| i. | ii. | iii. |
|
|
|
|
| iv. | v. | vi. |
|
|
|
|
| vii. | viii. | ix. |
|
|
|
|
| b) Common first aid and safety signage | ||
| x. | xi. | |